
The pKa1 of the carboxylic acid group of glycine is 2.34 and pKa2 of the amino group is 9.60, therefore, pI (glycine) (2.34+9.60)/2 5.94. The algorithms that calculate the isoelectric point of proteins and peptides use the [enderson Hasselbalch equation, and believe it or not, we have a henderson hasselbalch calculator that will tell you all about it. How do you calculate pI in chemistry Isoelectric point (pI) can be calculated using the formula, pI pKa1 + pKa2/ 2 for molecules with two ionizable groups (e.g.

The acidic amino acids have pI values between a pH of 5.0 to 7.0, while the basic amino acids have a higher pH to attain their isoelectric point. Let's look at the isoelectric points of specific biomolecules.Īmino acids are zwitterions when they attain their isoelectric point. It tells us when a particular molecule has attained the electrically neutral state, and the pI can affect the solubility of said molecule. The isoelectric point is an essential topic in chemistry and biochemistry. As long as you have any two of the three values to input, the calculator will work fine for you. Remember, our tool works in reverse and any other order you want to. Input these values in the calculator and the result is 6.55 6.55 6.55 Say you have molecule X, its p K a = 3.7 pKa = 3.7 p K a = 3.7 and p K b = 9.4 pKb = 9.4 p K b = 9.4. This value indicates the pH at which your molecule carries no net electric charge.
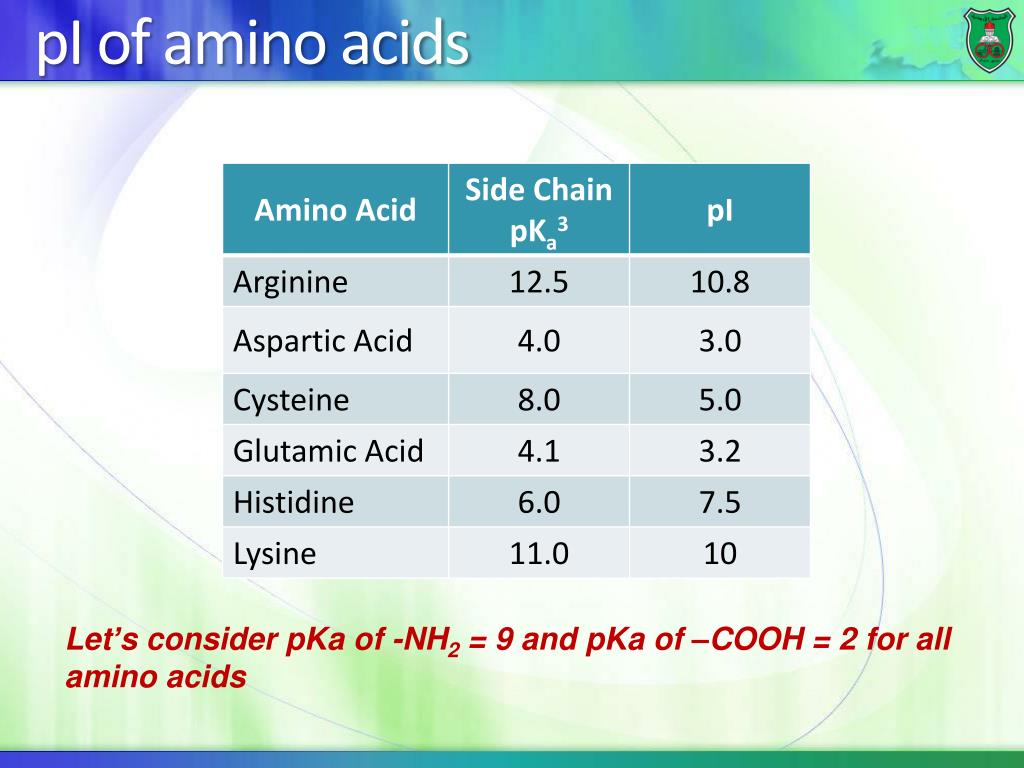
Calculate pi of amino acid how to#
Now, coming back to the point at hand, how to use the isoelectric point calculator? Follow the given steps, and that's it: The dissociation constant represents the capability of a substance to dissociate into ions in a solution. What are pKa and pKb values, you might wonder? These are the dissociation constants of acids and bases. It determines the isoelectric point of molecules based on their pKa and pKb values.

It also becomes more complicated for polyprotic groups, but all the groups in amino acids are monoprotic with water as a solvent.Our isoelectric point calculator is a tool you would love to use on the go. if one group becomes negatively charged, it becomes more "difficult" for the neighboring group to become negatively charged). This is only an approximation because there might be some cross talk between ionizable groups (i.e. The Henderson-Hasselbalch relationship describing each ionizable group is: I am asking for the expected value of the net charge (which would not be an integer) this number is relevant, for example, for the migration speed of the amino acid (or a protein) in gel electrophoresis or the strength of interaction with ion exchange chromatography media.įor example, a carboxylic acid/carboxylate group at a pH equal to its pKa would have an average charge of minus one half because half of the functional groups would be protonated (charge of zero) and half would be deprotonated (charge of minus one). Thus, when determining the average net charge across the ensemble (or a time-averaged charge of a single particle), you have to take this into account. When the pKa of one group (or more) is close enough to the pH, a fraction of the amino acids will be deprotonated at that group and the other fraction of amino acids will be protonated at that group in solution. When determining the charge of an amino acid, you have to take into consideration the pH and the pKa's of each of these groups. How do I determine the net charge of that amino acid when there are mixed protonation states of one or more of the groups at that pH (pKa of side chain, for example, is really close to the pH)?Īmino acids have terminal carboxyl and amino groups some amino acids have ionizable side chains. I am given an amino acid with an ionizable side chain at a certain pH.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
